Sheet Moulding Compound (SMC) is a thermosetting, fiber-reinforced molding compound made from crosslinkable resins, chopped glass fibers, mineral fillers, and functional additives. This ready-to-use, flowable sheet material enables the production of complex molded components with excellent surface finish. SMC is usually processed by hot pressing. The typical fiber length is 25-50 mm.
The formulation may differ depending on the type. On the European market, a distinction is generally made between the following types:
- Low Shrink: SMC with low reaction shrinkage, colorable. It is used in the construction and electrical industries.
- Low Profile: SMC with high surface quality, cannot be colored. Molded parts may have to be painted. Mainly used in the automotive industry.
- C-SMC: SMC that achieves very high strength values through targeted fiber orientation and special manufacturing processes such as profile drawing, winding, etc.
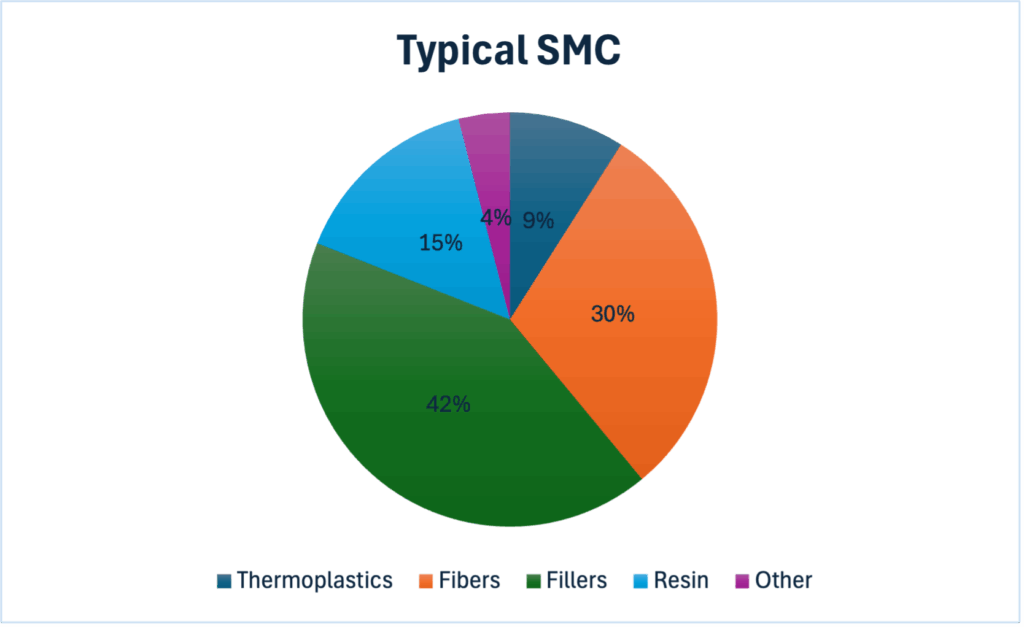
SMC can consist of the following components:
| Component | Explanation |
| Polyester or vinyl ester resin | Serves as a matrix |
| Thermoplastic additives | For shrinkage compensation |
| Mineral fillers | Fillers for cost reduction, shrinkage reaction and flame resistance |
| Organic peroxides | To control the hardening reaction |
| Inhibitors | To improve storage stability |
| Color pigments | For colour design |
| Fibers | Glass fibre, carbon fibre, natural fibre or polymer fibre |
| Additives | To control production properties, e.g. conductivity |
Properties of sheet moulding compound
The material properties depend on the respective SMC formulation. In general, however, the following properties are attributed to SMC:
- High mechanical strength
- High stiffness
- Weather resistance and UV resistance
- Electrically insulating
- Thermally insulating
- Fire-resistant (self-extinguishing properties)
- Chemical resistance
- High surface quality
Processing of sheet moulding compound
Processing is usually carried out using the hot pressing process. The SMC blanks are placed in heated steel tools and formed under pressure. This produces finished molded parts with high reproducibility in a short cycle time. Special, short-fiber BMC (Bulk Molding Compound) molding compounds, on the other hand, are suitable for injection molding. These are prepared in heated plasticizing units and injected into a mould. Injection moulding machines require special equipment for this process, in particular special plasticizing units. The tools also differ from those for thermoplastics.
Application of Sheet Moulding Compound
SMC is used in numerous industries – wherever mechanical performance, dimensional stability, and design flexibility are essential. Typical applications are:
- Automotive industry: exterior body panels, battery enclosures, underbody shields, trim covers
- Electrical engineering: housings for switchgear, insulators, covers
- Construction industry: facade panels, covers, installation boxes
- Sanitary engineering: shower trays, bathtubs, cover panels
Due to the combination of high strength and good surface quality, SMC is particularly suitable for visible molded parts with functional requirements.
Sources:
1. Handbuch Faserverbundkunststoffe/Composites, AVK – Industrieverreinigung Verstärkte Kunststoffe e.V. Hrsg.
2. Chemie.de: https://www.chemie.de/lexikon/Sheet_molding_compound